Top 10 Best Bud Food & Bloom Booster Fertilizers
The best nutrients for flowering cannabis. Most effective fertilizers for big buds (best bloom boosters). Get the high yields and save money by knowing what suitable flowering marijuana supplements contain.

Organic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers are made of natural ingredients. The highest concentration of plant nutrients comes from mineral powders, manures, and animal parts. Seaweed and molasses are also used in organic bud foods to promote beneficial bacteria and aid in growth processes. The presence of mycorrhizal fungi can help plants more easily absorb organic nutrients including Phosphorus.
Maxicrop

Overview: Seaweed-derived products are widely used in plant fertilizers for their growth-stimulating compounds. Many organic bloom boosters are based off kelp derivative and soluble potash. Save money on expensive liquid formulas by using kelp meal such as Maxicrop, made from harvested Norwegian kelp (Ascophyllum nodosum).
How it benefits flowering: NPK 0-0-17. A natural source of potassium and powerful biostimulants, Maxicrop contains more than 70 minerals, micronutrients, amino acids, and vitamins to help with bigger, more prolific blooms. Studies have shown that Maxicrop application increased plant root growth by 53–63%. It is also used for cloning and transplanting solutions due to the presence of vitamin B12.
Application: Dissolve 3 tablespoons of Maxicrop powder per gallon of water. Suitable for all cultivation methods. Don't spray buds, it will stick.
Mammoth P

Overview: Mammoth P is a microbial inoculant that utilizes beneficial bacteria and microorganisms to maximize phosphorus and micro-nutrient cycling for plant absorption. Developed at Colorado State University, Mammoth P has been proven to increase plant growth and crop productivity by independent labs.
How it benefits flowering: NPK 0-0-0. Live microbes in Mammoth P liberate bound phosphorus and produce enzymes that continually release nutrients to enhance plant health and boost yield.
Application: Refer to directions on bottle. Mix with water following the weekly application rate. Compatible for use as supplement in any plant feeding program.
Dr. Earth Organic Bud & Bloom Fertilizer

Overview: Dr. Earth's Flower Girl Organic Bud & Bloom booster is regarded as one of the best organic dry fertilizers for flowering buds. This mix contains and abundance of organic nutrient sources along with beneficial soil microbes and mycorrhizae to support healthy soils and high-yielding plants.
How it benefits flowering: NPK 3-9-4. Suitable as a stand-alone flowering fertilizer, Dr. Earth's Flower Girl has all the nutrients needed for blooming plants with microbial inoculant to improve soil health and crop yield.
Application: Use roughly 2 cups per inch of trunk diameter. Follow the labeled directions for detailed guidelines. Topdress, probe or mix it into soil medium.
BioThrive Bloom

Overview: BioThrive bloom is vegan plant food packed with a myriad of organic substances: alfalfa meal, cane sugar, copper sulfate, glacial rock powder, iron sulfate, kieserite, manganese sulfate, molasses, plant extracts, potassium sulfate, rock phosphate, sodium borate, sodium molybdate, soybean meal and zinc phosphate.
How it benefits flowering: NPK 2-4-4. BioThrive contains the essential nutrients for plant growth with a hearty dose of carbohydrates (sugars) known to stimulate beneficial microbial activity.
Application: Dilute 4 teaspoons of BioThrive per gallon of water. This liquid fertilizer is convenient for all types of growing, from hydroponics to in-the-ground soil application.
Happy Frog Bulb Food

Overview: FoxFarm's Happy Frog dry fertilizer is a mix of granular organic bud food ingredients such as bone meal, bat guano, and kelp meal. It's alive with beneficial soil microbes and mycorrhizal fungi inoculants that expand root development, helping plants feed more aggressively.
How it benefits flowering: NPK 3-8-8. Happy Frog Bulb Food adds humic acid (a natural byproduct of organic matter decomposition) as an organic chelating agent to help release the long-term nutrients in this fertilizer for plant absorption.
Application: Follow dosage instructions on the label for plant size. It can be mixed into potting mix before final transplant, probed into the root system, or layered onto the topsoil.
Synthetic Fertilizers
Synthetic fertilizers are made of various elemental compounds, mostly derived from the chemical chelation of minerals. The chelation process transforms these minerals into nutrients that plants easily absorb.
Synthetic nutrients work best in hydroponics, aeroponics, or an easy-flush, low-retention potting mix like 50% perlite, 50% vermiculite.
Jack's Classic Blossom Booster

Overview: J R Peters Jack's Classic Blossom Booster provides the essential NPK nutrients for flowering plants—plus micronutrients—all in an inexpensive water-soluble powder.
How it benefits flowering: NPK 10-30-20. This classic 1:3:2 nutrient ratio has proven to be the standard for blossom enhancers. A lot of hydro growers are ditching the expensive bottled nutrients and switching over to Jack's to save money.
Application: One tablespoon of powder per gallon of water. It can be used in any grow setup, including hydroponics and aeroponics.
Flower Fuel

Overview: Flower Fuel is a heavy-duty, high PK blossom booster that contains over 40 ingredients with nutrients, vitamins, hormones, amino acids, essential organic components, and every single micro and trace element.
How it benefits flowering: NPK 0-39-25. This type of high PK bloom booster is used throughout flowering to promote loads of resinous bud sites that develop into big buds right down to the stem.
Application: ¼ teaspoon per gallon of water. The 250 gram container treats 200 gallons of water. Suitable for any soil, coco, hydroponic or aeroponic system.
Grow More Hawaiian Bud & Bloom

Overview: A hard-hitting nutrient "boom!" for plants, Grow More Hawaiian Bud & Bloom is packed with extremely high amounts of phosphorus, a hearty dose of potassium, a little nitrogen, and chelated micronutrients.
How it benefits flowering: NPK 5-50-17. Potent PK fertilizers like Hawaiian Bud & Bloom will help plants stack up heavily with multiple bud sites. This contributes to heavy yielding, big bud harvests when applied correctly.
Application: Suggested use varies at ¼–1 teaspoon per gallon of water. Just be careful of burning plants by overfeeding.
FoxFarm's Liquid Bloom Trio

Overview: The liquid bloom trio by FoxFarm is a very popular fertilizer in the cannabis growing community. Big Bloom is all organic, while Tiger Bloom and Grow Big contain synthetic nitrates and phosphates.
How it benefits flowering: These three bottles are sold together in a fully balanced bud flowering formula. They contain readily available nutrients combined with organic ingredients and active microbes.
Application: 2–4 teaspoons per gallon of water. FoxFarm liquid fertilizers can be used in soils, pots, hydroponics, and aeroponics.
Osmocote Smart-Release Plant Food

Overview: Most synthetic fertilizers are readily available, meaning they do not last long after application and need to be reapplied regularly for best results. Osmocote Smart-Release Plant Food is a controlled release granule fertilizer that feeds plants for up to 4 months.
How it benefits flowering: NPK 14-14-14. Balanced, long-term synthetic fertilizer high in nutrients. Each granule is coated with a resin that controls nutritional release. A favorite of old-school guerilla growers.
Application: Sprinkle 1 scoopful of Osmocote per 2 gallons of growing medium and work it into the top 1–3 inches.

What Nutrients Does Cannabis Need to Grow?
Nutrients are used as food by plants. Cannabis requires large amounts of mineral nutrients to compose its leaves and dense flowers. The best nutrients for cannabis are, in fact, the nutrients which the plant uses to support growth.
- Well-fed cannabis plants are green and healthy, leading to increased flower production and higher yields of bigger buds. Well-fed plants have a stronger immunity to disease than underfed plants.
- Underfed cannabis plants are often slow to grow, stunted, yellowing, and frail. The buds develop sparsely and produce lower quality and yield than well-fed plants. Underfed plants have a weak immune system due to a lack of nutrients.

There are six major nutrients that cannabis plants require to grow—three of which are obtained from the air and water:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2) - Plants absorb CO2 from the air, combining it with water and light to make carbohydrates—a process more commonly known as photosynthesis.
- Hydrogen (H) - Hydrogen is a part of water (H2O). As plants absorb water, they split the water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen using the energy from the sun.
- Oxygen (O) - Along with what has been described above, plants consume oxygen through their pores—even at night. This is what's called respiration. Respiration combines oxygen and the food created during photosynthesis to produce usable energy for plants.
The other three nutrients are Nitrogen (N), Potassium (P), and Phosphorus (K). These nutrients are mostly obtained through a plant's roots but can also be absorbed through tissue (i.e., foliar feeding).
Major Nutrients (N-P-K)
What are the three numbers labeled on fertilizers?
NPK (short for Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium) are the major nutrients that plants absorb through their roots or vascular tissue. NPK are the three numbers you see labeled on the front of commercial fertilizers.

The numbers represent the percentage of a nutrient a fertilizer is made of. For example, a 50-kg bag of 12-24-12 fertilizer is composed of 12% N, 24% P, and 12% K. To figure out how much K that is you can multiply the weight by the percentage: 50 kg × 0.12 = 6 kg of K.

Nitrogen (N)
- Nitrogen (a gas) is a major component of amino acids (the building blocks of proteins) and chlorophyll (the energy substance made by plants through photosynthesis). Nitrogen is the most utilized nutrient of a plant's life-cycle, especially during its early stages of growth.
- Organic sources of N are plant litter, compost, manure, blood meal, feather meal, etc.
- Synthetic derivatives of N include formulations of urea and ammonium nitrates.
Using Nitrogen for flowering cannabis:
High nitrogen fertilizers have a pronounced effect on cannabis plants, often triggering vertical growth. This is why only moderate nitrogen levels are applied to blooming cannabis plants to keep their buds hard, dense, and compact. Cannabis fertilizers with a high nitrogen ratio are usually 'veg' nutrients intended for the early stages of growth.

Phosphorus (P)
- Phosphorus (a mineral element) is a component of plants' complex nucleic acid structure, which regulates protein synthesis. It is important in cell division and the development of new tissue, also associated with complex energy transformations in the plant. Phosphorus lets plants use the energy harnessed by photosynthesis to drive their metabolism.
- Organic sources of P include soft rock phosphate, bat guano, steamed bone meal, fish bone meal, and crushed granite.
- Synthetic derivatives of P are made by treating rock phosphate with either sulfuric acid or phosphorus acid.
Using Phosphorus for flowering cannabis:
High phosphorus availability to plants can lead to additional flower (bud) sites and a healthy root system. The most critical time for cannabis plants to utilize phosphorus is during the beginning of their blooming process (first white hairs), as this is when a big energy change happens in the plant. Cannabis fertilizers with a high phosphorus ratio are often used as flowering nutrients, meant for the mid–late stages of growth.

Potassium (K)
- Potassium (a mineral element) triggers the activation of different growth-related enzymes, important in many chemical processes taking place during flower production. It also regulates the opening and closing of stomata (pores) during photosynthesis, in part controlling CO2 uptake. Potassium is attributed to playing a major part in the absorption and movement of water, nutrients, and carbohydrates in plant tissue.
- Organic sources of K include soluble potash (ashes), manures, compost, molasses, and kelp meal.
- Commercially-used K like muriate of potash and sulfate of potash are salts that make up part of ocean saline deposits.
Using Potassium for flowering cannabis:
Potassium is a catalyst for carbohydrate metabolism, so when you want your marijuana plants to pack on the carbs, high levels of K are important. Potassium rivals nitrogen as the nutrient absorbed in the greatest amounts by plants. It's best to increase K levels during the midst of a plant's flowering cycle; healthy amounts of potassium will lead to hard, thick, and heavy bud yields. Cannabis fertilizers containing a high potassium ratio are usually flowering nutrients used in the mid–late growth stages.
Minor and Micro-Nutrients
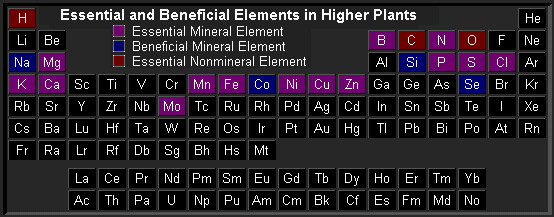
Minor and micro-nutrients are essential for healthy plant growth, just used in smaller amounts by plants hence the name.
There are three nutrients classified as minor nutrients. These are:
- Calcium (Ca) - has a regulating effect in the cells and contributes to the stability of the plant, important in the development of cell walls.
- Magnesium (Mg) - is a building block of chlorophyll, essential to the process of photosynthesis. Without magnesium, plants cannot process sunlight.
- Sulfur (S) - is used in the formation of amino acids, proteins, and oils. Sulfur helps develop and activate different vitamins and enzymes.
Seven elements are needed in tiny amounts; these are dubbed micronutrients.
- These include boron (B), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), molybdenum (Mo), zinc (Zn), nickel (Ni), and chloride (Cl).
- Being deficient in any of these micronutrients can impair growth.
What are Effective Flowering Fertilizers?

The best bloom boosters, bud foods, and flower fertilizers are terms for the right nutrient additives meant to be used when a plant produces flowers (buds). These nutrients are available to plants in the form of organic material (organic fertilizers) or are derived through chemistry procedures (synthetic fertilizers).
What do the best bloom fertilizers have in common?
High proportions of Phosphorus (P) and Potassium (K) to maximize bud formation & growth-related enzymes in the plant.
Low proportions of Nitrogen (N) to prevent bud stretching.
Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg) are utilized to aid in dense flower clustering, along with other minor nutrients, micronutrients, and trace minerals.

Cannabis Fertilizer Ratio
NPK ratio recommendations for crops are typically provided to farmers via a university extension office. As a rule of thumb, cannabis may follow similar NPK guidelines as those given for tomatoes.
A high-N starter fertilizer is provided during the early growth (veg cycle) to promote vigorous growth. In contrast, a high-PK bloom fertilizer is given during the later growth (flowering cycle) to support budding.
Cannabis growers tend to ween off nitrogen as the plant gets closer to harvest time. For example, low-N, high-PK fertilizer near 1:3:2 ratio (2-6-4, 4-12-6, etc.) will be used for the early and mid flowering cycle, while PK-only fertilizer (0:1:1 or 0:3:2 NPK ratio) is applied towards the end of flowering.

Organic vs. Synthetic Nutrients
Organic cannabis fertilizers contain both readily available and long-term nutrient sources. A thriving microbial ecosystem will help plants access these nutrients faster.
Synthetic cannabis fertilizers are readily available nutrients (except for controlled-release fertilizer). These contain chemically chelated nutrients for immediate absorption by plants.

Cannabis Fertilizer Burn
Over-application of fertilizer nutrients on cannabis plants can lead to "fertilizer burn" or "tip burn"—desiccation of plant tissues seen as a leaf scorching due to the osmotic stress caused by over-fertilizing.
Avoid fertilizer burn by following the recommended application guidelines on fertilizer product labels. Cannabis plants that show signs of fertilizer burn should be 'flushed' with a long watering to rid excess nutrients from the root zone.

Nutrient Lockouts
When applying high amounts of fertilizer, it's important to consider the possibility of a nutrient lockout. This can occur from pH imbalance or excess nutrient buildup. Buildup often happens in mediums that can not be flushed clean of P, as this nutrient tends to cling to other particles in the soil.
When too much P is present in the soil, it binds up calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, and zinc, making these nutrients unusable. Excess P also has harmful effects on beneficial soil organisms such as mycorrhizal fungi.
Compost and Worm Castings as Fertilizer?

There are benefits to using organic matter in soil like increasing water and nutrient holding capacity of the soil, improving soil structure, and promoting beneficial microbes.
Compost is often analyzed as a 1-1-1 dilutant fertilizer. However, all compost varies in composition. The nutrient profile of compost depends on what was used to make it.
Worm casting compost made with eggshells (calcium) and banana peels (potassium) is a great DIY organic bud food that you can make at home.
Disclaimer: We do not promote or undertake in illegal activities. Refer to our Privacy Policy for more information.




Comments
Replying to @Dino
Replying to @Dino
Replying to @James wilson
Replying to @Maxime
Replying to @Jon Dodson
Replying to @Brian mc
Replying to @Brian mc
Replying to @Brian mc
Replying to @Shawn Bettencourt
Replying to @Bak2006
Replying to @R.J. Castelan
Replying to @Ken
Replying to @Hot rod
Replying to @Hot rod